The manufacturing industry has undergone profound changes over the past few decades, but none have been as transformative as the advent of robotics and automation. These technologies are not just enhancing efficiency; they are fundamentally reshaping the way manufacturing operates. As we move into 2024, the impact of robotics and automation is expected to grow even more significant. This article explores the key trends in robotics and automation that are transforming modern manufacturing and what to expect in the near future.
1. The Rise of Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human operators in a shared workspace. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which operate in isolation, cobots are built with safety features that allow them to work safely near humans. This trend is gaining momentum as manufacturers seek to combine the precision and strength of robots with the creativity and problem-solving abilities of human workers. In 2024, we can expect to see an increase in the deployment of cobots across various manufacturing sectors, from automotive to electronics.
Benefits of Collaborative Robots:
- Increased Flexibility: Cobots can be easily reprogrammed and adapted for different tasks, making them ideal for small-batch production and frequent changes in manufacturing processes.
- Enhanced Safety: Advanced sensors and safety systems ensure that cobots can operate safely alongside human workers, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Cost Efficiency: Cobots are typically more affordable than traditional robots, offering a cost-effective solution for manufacturers looking to automate specific tasks without investing in large-scale automation systems.
2. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is increasingly being integrated into robotics and automation systems. AI enables robots to perform complex tasks by learning from data, making real-time decisions, and adapting to new situations. This integration is driving significant improvements in manufacturing efficiency and quality control.
Key Applications of AI in Manufacturing:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze data from machinery to predict potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Quality Control: AI-powered vision systems can detect defects and inconsistencies in products with high accuracy, ensuring higher quality standards.
- Process Optimization: AI helps optimize manufacturing processes by analyzing performance data and identifying opportunities for improvement, leading to increased productivity and reduced waste.
3. Advanced Robotics with Enhanced Capabilities
The capabilities of robots have evolved dramatically, with advancements in materials, sensors, and software enabling them to perform increasingly complex tasks. In 2024, we will see robots with enhanced dexterity, precision, and versatility entering the manufacturing floor.
Notable Developments in Robotics:
- Soft Robotics: Soft robots, made from flexible materials, are capable of handling delicate objects and performing tasks that require a gentle touch. This technology is particularly useful in industries such as food processing and electronics.
- Exoskeletons: Wearable robotic exoskeletons assist human workers in lifting heavy objects and performing repetitive tasks, reducing strain and fatigue.
- Swarm Robotics: Inspired by the behavior of social insects, swarm robotics involves the use of multiple robots working together in coordinated ways to complete tasks more efficiently.
4. The Growth of Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems. In manufacturing, digital twins are used to simulate and analyze the performance of production lines and machinery in real-time. This technology provides valuable insights into how systems operate, allowing manufacturers to optimize processes and predict outcomes.
Benefits of Digital Twins:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Digital twins provide real-time data on the performance of manufacturing systems, enabling quick responses to issues and improving operational efficiency.
- Simulation and Testing: Manufacturers can test different scenarios and configurations in a virtual environment before implementing changes in the physical world, reducing the risk of costly errors.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By analyzing data from digital twins, manufacturers can make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and process improvements.
5. Expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a crucial role in modern manufacturing by connecting machines, sensors, and devices through the internet. This connectivity allows for real-time data collection and analysis, leading to smarter and more efficient manufacturing processes.
IoT Applications in Manufacturing:
- Smart Sensors: IoT-enabled sensors monitor various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, providing valuable data for process control and maintenance.
- Automated Inventory Management: IoT systems track inventory levels and manage supply chains in real-time, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Manufacturers can remotely monitor and control machinery and processes from anywhere, increasing flexibility and responsiveness.
6. Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency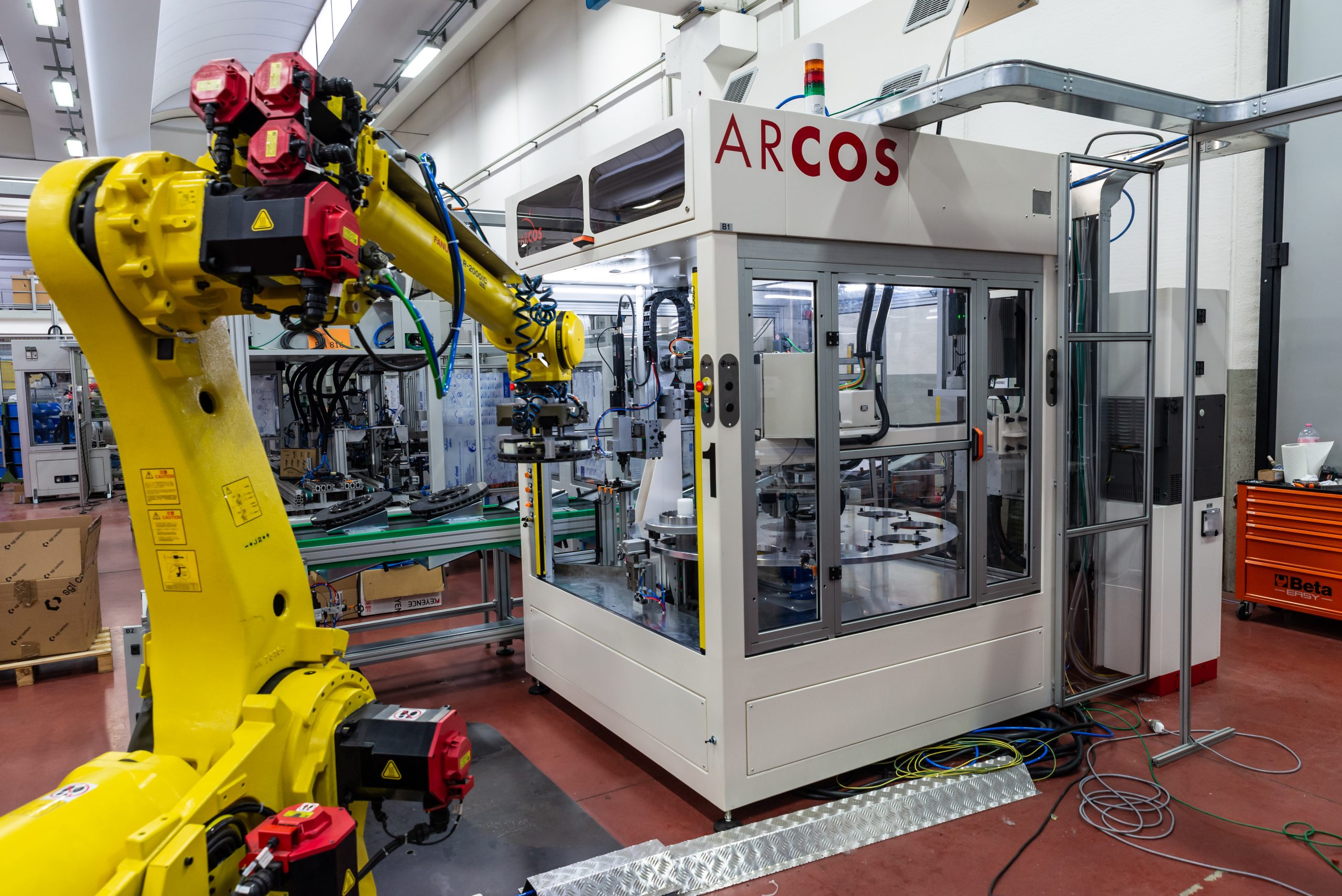
As manufacturers strive to reduce their environmental impact, robotics and automation are being leveraged to improve sustainability and energy efficiency. These technologies contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices by optimizing resource usage and reducing waste.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices:
- Energy-Efficient Robots: Modern robots are designed to consume less energy while maintaining high performance, contributing to reduced operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Waste Reduction: Automated systems help minimize material waste by improving precision and accuracy in manufacturing processes.
- Recycling and Reuse: Robotics can assist in sorting and processing recyclable materials, supporting circular economy initiatives.
7. The Shift Towards Customization and On-Demand Production
Consumer demand for personalized and custom products is driving the shift towards on-demand production. Robotics and automation enable manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market trends and customer preferences.
Advantages of On-Demand Production:
- Increased Flexibility: Automated systems can easily switch between different product designs and configurations, allowing for greater customization and shorter lead times.
- Reduced Inventory Costs: On-demand production reduces the need for large inventories, lowering storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolete stock.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: The ability to offer customized products meets consumer demands for uniqueness and personalization, improving customer satisfaction.
8. Workforce Transformation and Skills Development
The integration of robotics and automation is transforming the manufacturing workforce. While some traditional jobs may be displaced, new opportunities are emerging for workers with skills in robotics, programming, and data analysis.
Key Trends in Workforce Transformation:
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Manufacturers are investing in training programs to equip employees with the skills needed to operate and maintain advanced robotic systems.
- Collaboration Between Humans and Robots: The role of human workers is evolving to focus on tasks that require creativity, problem-solving, and supervision of automated systems.
- New Job Opportunities: The growth of robotics and automation creates new job roles in areas such as robotics engineering, AI development, and data analysis.
Conclusion
The transformation of modern manufacturing through robotics and automation is driven by several key trends that promise to shape the industry in 2024 and beyond. Collaborative robots, AI integration, advanced robotics, digital twins, IoT expansion, sustainability, on-demand production, and workforce transformation are all contributing to a more efficient, flexible, and responsive manufacturing landscape. As these technologies continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay abreast of these trends to remain competitive and capitalize on the opportunities presented by this new era of manufacturing.

