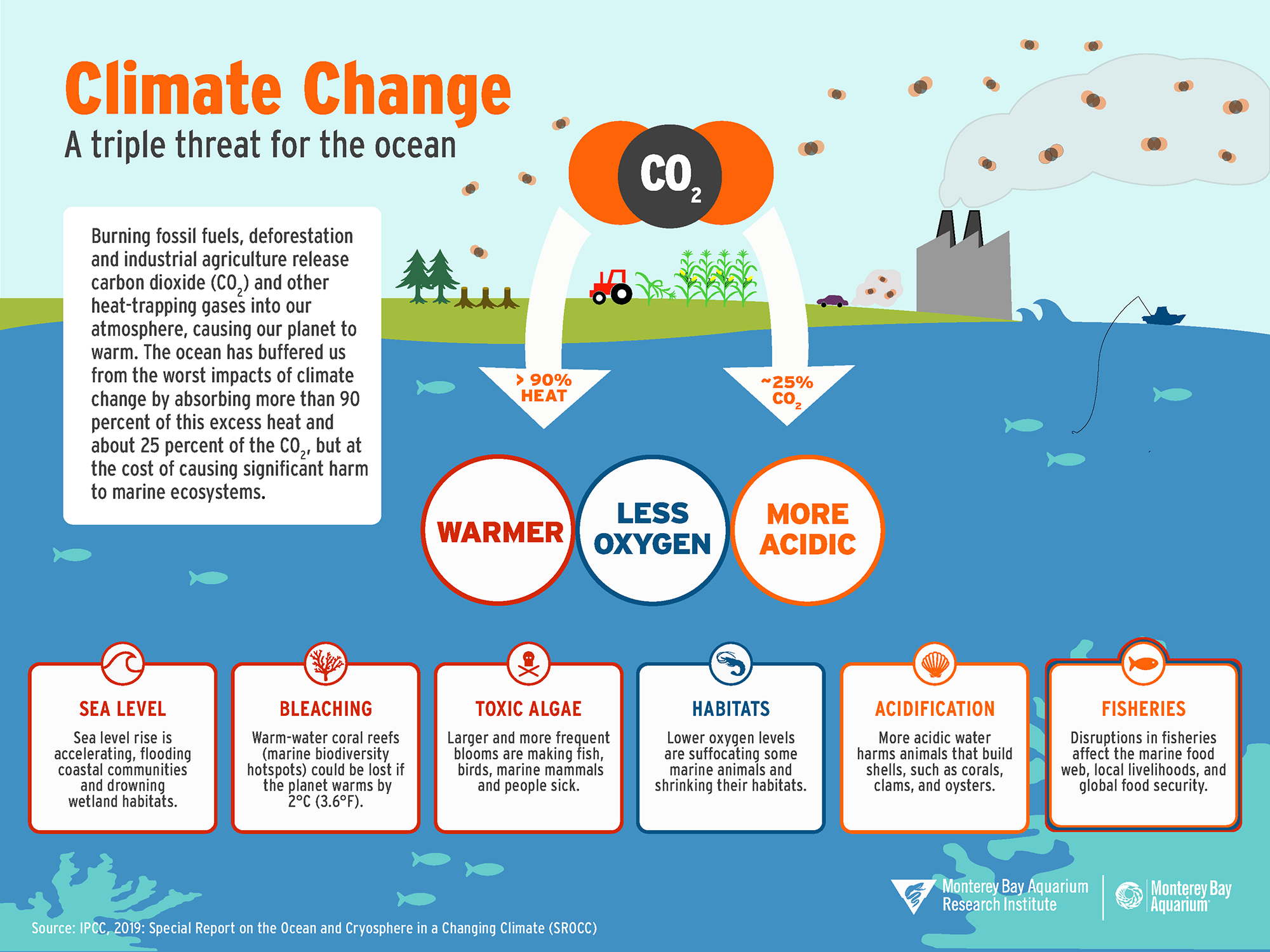
Climate change is undeniably one of the most pressing challenges of our time. It poses significant risks to natural ecosystems, human health, and the global economy. As the planet continues to warm, the impact of climate change becomes more evident, manifesting in various forms. In this article, we will explore the top three climate risks facing our world today and their cascading effects.
1. Extreme Weather Events
a. Increasing Frequency and Intensity
One of the most noticeable consequences of climate change is the rise in extreme weather events. Hurricanes, typhoons, floods, droughts, and heatwaves are occurring more frequently and with greater intensity. These events not only cause immediate destruction but also have long-term repercussions.
b. Economic Impact
Extreme weather events lead to significant economic losses. Infrastructure damage, crop failures, and business interruptions can cost billions of dollars. For example, the 2017 hurricane season in the United States, which included Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria, caused an estimated $306 billion in damages. These costs place a heavy burden on governments, businesses, and individuals.
c. Human Health and Safety
The impact on human health and safety is profound. Extreme heatwaves can lead to heat-related illnesses and deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. Flooding and storms can cause injuries, displacement, and loss of life. Additionally, the stress and anxiety associated with these events can have lasting mental health effects.
2. Sea Level Rise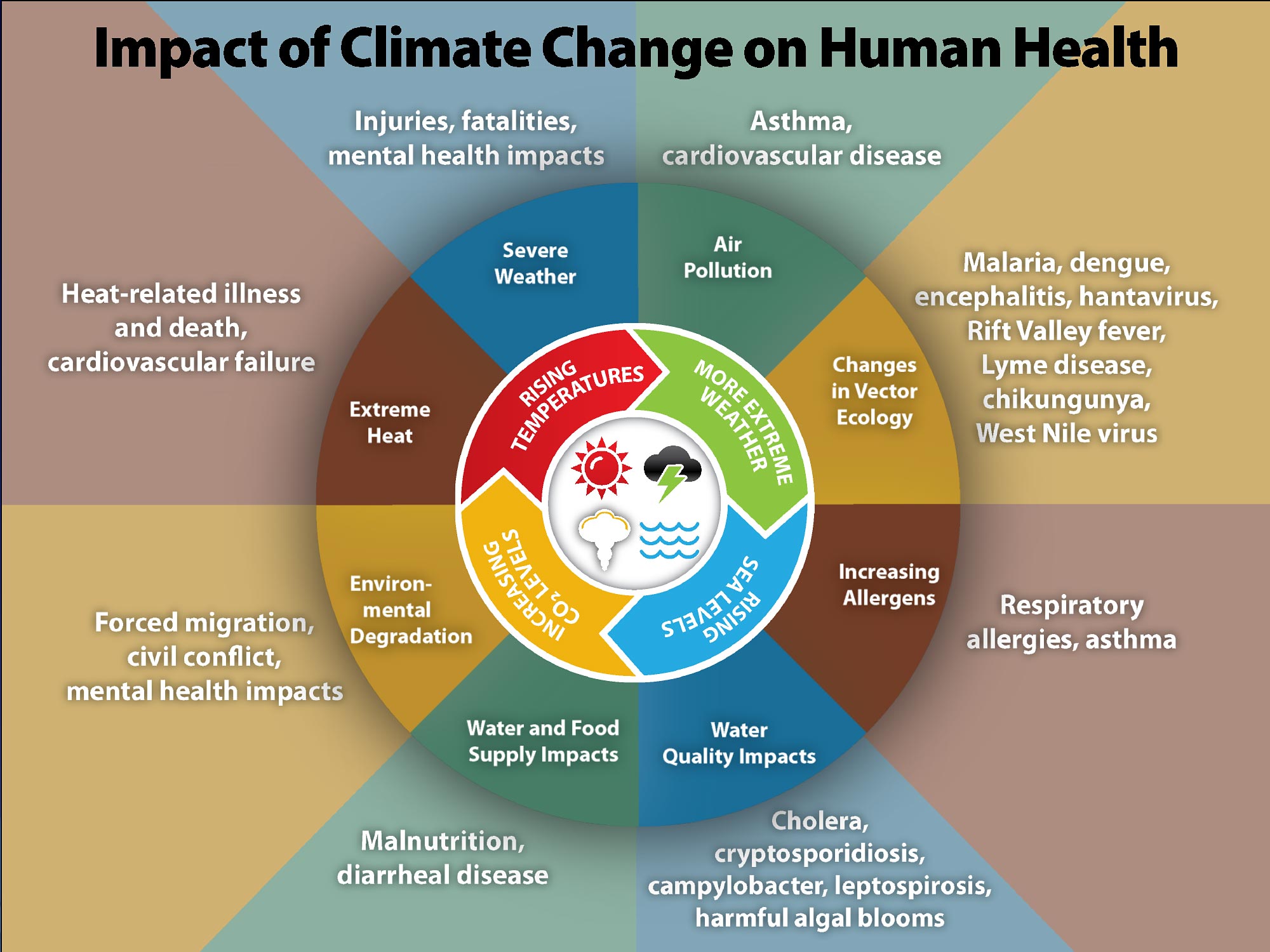
a. Melting Ice Caps and Glaciers
As global temperatures rise, polar ice caps and glaciers are melting at an alarming rate. This melting contributes to sea level rise, which threatens coastal communities around the world.
b. Coastal Erosion and Flooding
Sea level rise leads to increased coastal erosion and more frequent and severe flooding. Coastal cities, such as Miami, New York, and Bangkok, are at risk of becoming partially submerged. This not only threatens homes and infrastructure but also freshwater supplies, as saltwater intrusion contaminates coastal aquifers.
c. Displacement and Migration
The rising sea levels force communities to relocate, leading to displacement and migration. Small island nations like the Maldives and Tuvalu are particularly vulnerable, facing the possibility of becoming uninhabitable. This displacement can lead to overcrowding in other areas, strain resources, and cause socio-political tensions.
3. Biodiversity Loss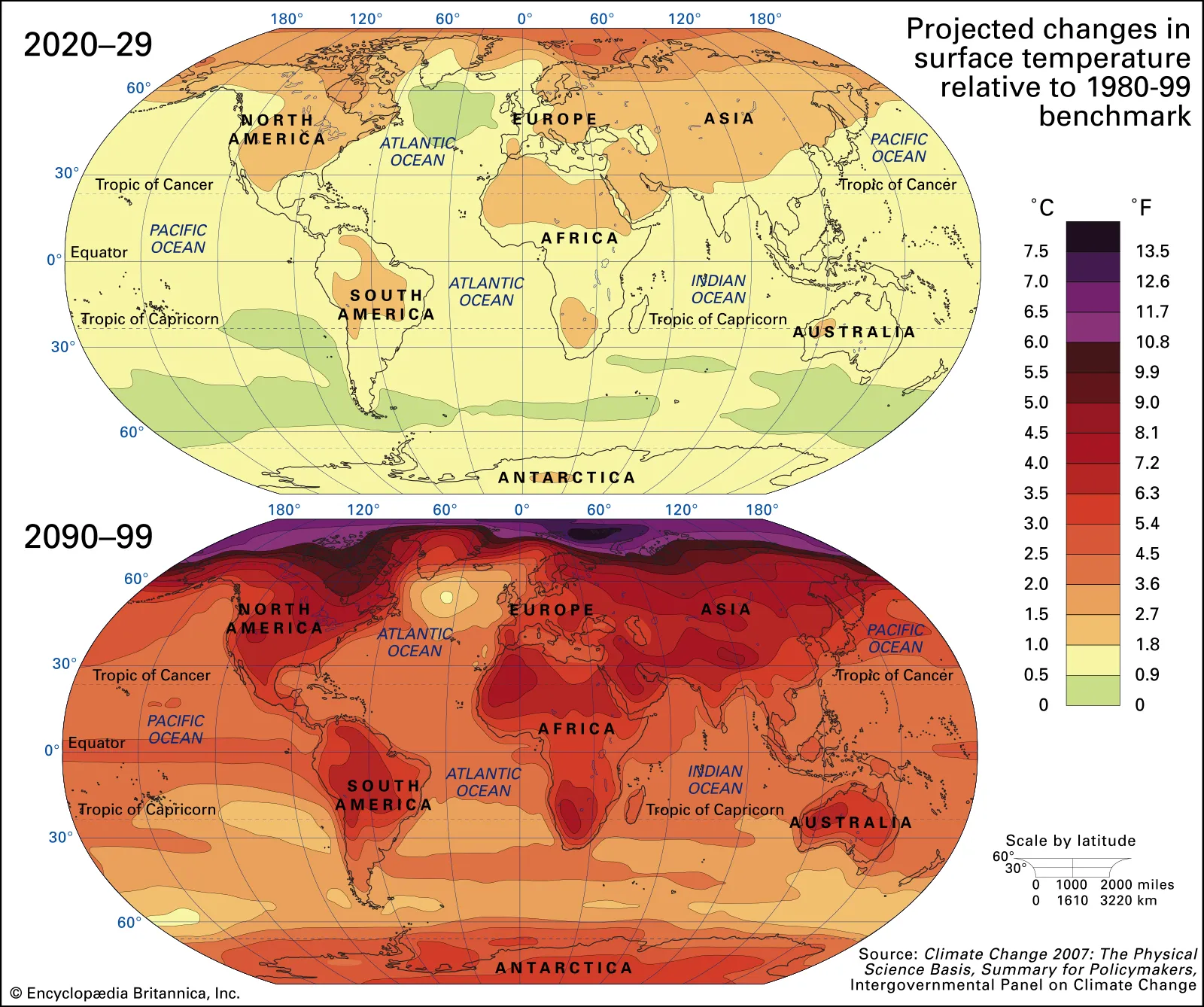
a. Habitat Destruction
Climate change contributes to habitat destruction, altering ecosystems and threatening biodiversity. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns disrupt habitats, making them unsuitable for many species. For instance, coral reefs are highly sensitive to temperature changes, and bleaching events have become more common, leading to the loss of these vital ecosystems.
b. Species Extinction
The loss of habitats and changing environmental conditions put many species at risk of extinction. Polar bears, for example, are losing their sea ice habitat, which they rely on for hunting seals. Similarly, amphibians are highly vulnerable to climate change, with many species already facing extinction.
c. Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity loss affects ecosystem services that are crucial for human well-being. These services include pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration. The decline in pollinator populations, such as bees, can severely impact agriculture and food security. Forests, which act as carbon sinks, are under threat from changing climate conditions, reducing their ability to mitigate climate change.
Cascading Effects
a. Food Security
The combined impact of extreme weather events, sea level rise, and biodiversity loss poses a significant threat to food security. Crop yields can be reduced by floods, droughts, and changing climatic conditions, leading to food shortages and increased prices. This is particularly concerning for developing countries that rely heavily on agriculture.
b. Water Scarcity
Climate change affects the availability and distribution of freshwater resources. Melting glaciers and reduced snowpack diminish water supplies for regions that depend on these sources. Additionally, altered precipitation patterns can lead to droughts, further exacerbating water scarcity. This scarcity impacts drinking water, agriculture, and industry.
c. Economic Instability
The cascading effects of climate risks can lead to economic instability. The costs associated with disaster recovery, infrastructure repair, and adaptation measures are substantial. Additionally, the loss of productivity due to health impacts and displacement can hinder economic growth. This instability can be particularly challenging for developing economies with limited resources.
Conclusion
The top three climate risks facing our world today—extreme weather events, sea level rise, and biodiversity loss—are interconnected and have cascading effects on various aspects of life. Addressing these risks requires urgent and coordinated global action. Mitigation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, along with adaptation strategies, are essential to protect our planet and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.